Establishing and maintaining proper accounting practices forms the cornerstone of successful business operations in Chile. The Chilean tax and accounting system, administered primarily by the Internal Revenue Service (Servicio de Impuestos Internos - SII), combines comprehensive compliance requirements with increasingly digital administration processes. Understanding these obligations from the outset enables companies to build robust financial management systems that support both regulatory compliance and strategic decision-making.
Foundational Accounting Principles and Requirements
Chile's fiscal year aligns with the calendar year, running from January 1st through December 31st. All corporate entities must prepare annual financial statements for shareholder review and regulatory compliance. The accounting system mandates Spanish as the primary language and Chilean pesos as the standard currency, though exceptions may be granted under specific circumstances.
The comprehensive digitalization of Chile's accounting environment represents a significant characteristic of the current system. Electronically issued and received documents integrate directly into accounting systems, while transactions lacking formal documentation require manual entry. This digital framework facilitates real-time monitoring by tax authorities and demands corresponding technological adaptation from businesses.
【Lawshi Professional Insight】
The mandatory digital accounting environment in Chile requires businesses to implement compatible software solutions from inception. Companies should ensure their accounting systems can interface directly with SII platforms to avoid compliance gaps. The electronic trail created by these systems enables tax authorities to conduct automated cross-checks, making consistency across all reporting crucial.
Pre-Operational Compliance Requirements
Before commencing business activities, companies must complete three essential administrative procedures. The Tax Identification Number (RUT) serves as the foundational business identifier and must be obtained following company registration. Subsequently, companies must file a Declaration of Initiation of Activities with the SII, disclosing capital information and legal addresses.
Municipal licensing represents the third critical prerequisite, with requirements varying by location and business activity. Each physical establishment—including offices, warehouses, and retail locations—requires separate authorization from the relevant municipality.
【Lawshi Practical Tip】
The municipal licensing process often involves unexpected delays due to local regulatory variations. We recommend initiating this process immediately after securing your RUT, as operating without proper municipal authorization can result in significant penalties and operational disruptions. Early engagement with local municipal authorities can help identify specific requirements for your business category.
Income Tax Framework and Residency Considerations
Chile employs a residence-based taxation system for individuals and entities. Companies incorporated in Chile face worldwide income taxation, while individuals establishing Chilean residency benefit from a three-year transition period during which only Chilean-source income remains taxable.
The determination of tax residency follows specific criteria, with individuals potentially qualifying as residents through either demonstrated permanent intent or physical presence exceeding six months within a calendar year or across two consecutive years. Chilean-source income encompasses revenue generated from assets located within Chilean territory or activities conducted therein.
Value Added Tax Administration
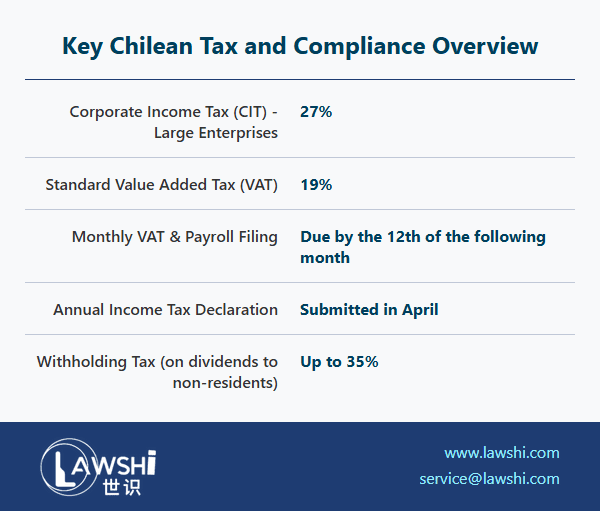
Chile's Value Added Tax system imposes a standard 19% rate on domestic transactions, embedded within the final consumer price. The mechanism operates through a credit-debit system where purchasing entities accumulate VAT credits while selling entities accumulate VAT debits. The net difference determines the monthly VAT liability.
Export-oriented businesses benefit from significant VAT exemptions, extending beyond goods to include specific services such as international transportation and specialized scientific activities. The monthly declaration and payment process occurs exclusively through digital platforms, with strict deadlines typically falling on the 12th day of the following month.
Comprehensive Bookkeeping Obligations
Chilean companies must maintain complete accounting records including standard financial documentation such as cashbooks, journals, ledgers, and balance sheet registers. Specific tax registers require separate maintenance, covering sales, purchases, payroll, tax withholdings, inventory, and taxable profits.
All accounting and tax books require formal stamping by the SII before use. While traditional bound volumes remain acceptable, computerized systems have gained prevalence following specific authorization procedures. Recent regulatory updates have simplified foreign currency accounting for qualifying businesses, reflecting Chile's increasingly international business environment.
【Lawshi Exclusive Service】
Our firm provides comprehensive accounting system setup and compliance monitoring services tailored to Chile's regulatory environment. We assist clients in selecting and implementing SII-compatible accounting software, establishing proper record-keeping protocols, and developing internal controls that ensure ongoing compliance while supporting business intelligence needs.
Strategic Compliance Planning
The integrated nature of Chile's tax system necessitates coordinated approaches to compliance management. Companies should develop systematic processes that address both national-level tax obligations and municipal requirements, recognizing that compliance failures in one area can trigger broader regulatory scrutiny.
The digital transformation of Chile's tax administration continues advancing, with businesses benefiting from implementing scalable accounting systems capable of adapting to evolving reporting requirements. Proactive compliance planning, including regular internal reviews and system updates, helps prevent operational disruptions while optimizing tax positions.
Chile's accounting framework, while comprehensive, provides clarity and predictability for businesses that invest in understanding its requirements and implementing appropriate systems. The structured approach to compliance, combined with increasingly digital administration, creates an environment where properly prepared businesses can operate efficiently while meeting their regulatory obligations.
