Argentina has positioned itself as an increasingly attractive destination for foreign investment, with the World Bank's Doing Business Report highlighting the country's streamlined business establishment process. Compared to regional averages, Argentina offers significantly faster company registration timelines and competitive startup costs. This guide provides essential insights into Argentina's corporate legal environment to assist international investors in making informed market entry decisions.
Corporate Establishment Process
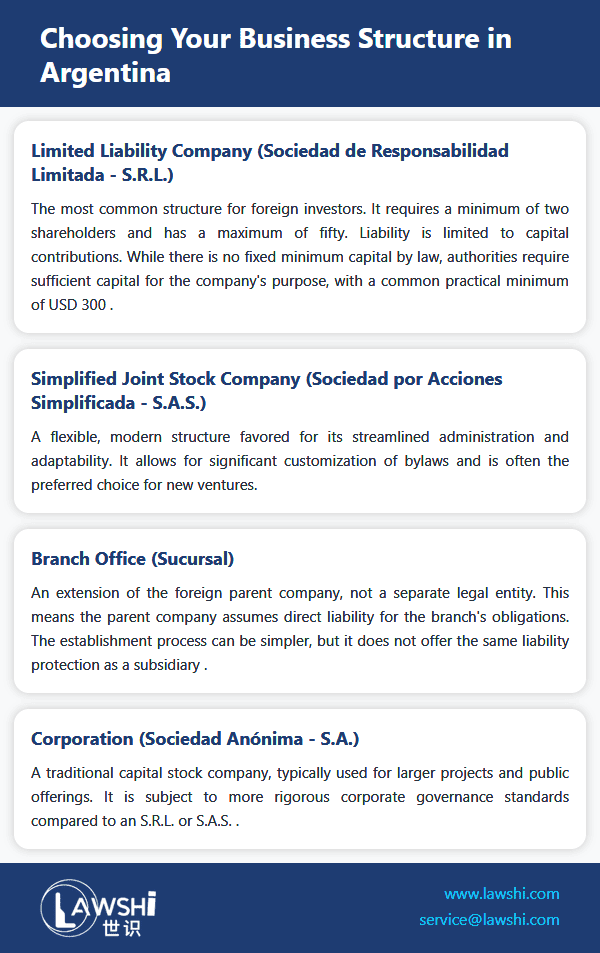
The initial phase of establishing a corporate presence in Argentina involves three fundamental steps that set the foundation for successful market entry. First, investors must select the most appropriate entity type that aligns with their strategic objectives and investment scale. The Argentine legal framework provides multiple options, each with distinct characteristics governing liability, governance, and operational flexibility.
【Lawshi Professional Insight】
The selection of entity type represents a critical strategic decision with long-term implications for tax planning, liability exposure, and operational flexibility. Many foreign investors initially favor the Simplified Joint Stock Company (Sociedad por Acciones Simplificada) due to its streamlined administration and adaptability, though specific business objectives may warrant consideration of alternative structures.
Name verification and reservation constitute the subsequent steps in the establishment process. Through the Public Registry of Commerce (Inspección General de Justicia or IGJ), investors can verify name availability and secure reservation through the "Control of Homonymy" mechanism. The reservation requires confirmation within a 30-day window to maintain validity, necessitating efficient progression through subsequent registration stages.
Structured Investment Pathways
Argentina's legal framework offers five distinct pathways for foreign investment, each designed to accommodate different strategic objectives and operational requirements.
Branch Establishment
Foreign corporations may establish branches as extensions of their parent entities, operating under the legal framework of their home jurisdiction while complying with Argentine registration requirements. Unlike subsidiary formations, branches do not constitute separate legal entities, creating direct liability exposure for the parent organization.
【Lawshi Practical Tip】
While branches offer simplified establishment processes, the absence of legal separation means parent companies assume direct responsibility for all Argentine operations. We recommend maintaining detailed separation between head office and branch accounting records and implementing clear internal controls to manage this exposure.
The branch registration process requires comprehensive documentation, including legalized and apostilled head office documents, representative identification, and political exposure declarations. The requirement for Official Gazette publication ensures transparency but adds to the establishment timeline.
Equity Participation Structures
Foreign entities seeking ownership positions in Argentine companies must complete registration with the IGJ and relevant provincial registries. This pathway creates distinct legal separation between the foreign investor and local operations, limiting liability to the invested capital while establishing an independent Argentine legal presence.
Local Entity Formation
The creation of new local entities involves detailed bylaws development, capital deposition, and regulatory compliance. Bylaws must comprehensively address governance, capital structure, profit distribution, and dissolution procedures. Capital requirements vary by entity type, with some structures permitting partial initial deposits while others mandate full capitalization at inception.
【Lawshi Exclusive Service】
Our firm provides end-to-end support for local entity formation, including customized bylaws drafting that balances compliance requirements with operational flexibility. We facilitate capital deposition procedures and manage the complete registration process with relevant authorities to ensure timely market entry.
The publication requirement in Argentina's Official Gazette serves as a public notice mechanism, while the subsequent registration process involves submission of comprehensive documentation to the IGJ and provincial authorities.
Acquisition of Existing Operations
Investors may pursue strategic entry through acquisition of established local companies. This pathway involves rigorous due diligence, structured negotiation through letters of intent, and detailed transfer procedures that vary by entity type. Corporations require specific shareholder registry updates and potential governance changes, while limited liability companies face distinct registration requirements for ownership transfers.
Business Asset Acquisition
The purchase of business assets or "goodwill" represents an alternative approach that focuses on operational components rather than equity transfer. This method typically avoids assumption of hidden liabilities, though specific procedures must be followed to achieve this protection. The process involves detailed liability disclosure, public notification, and creditor opposition periods that require careful management.
Ongoing Compliance Obligations
Following successful registration, entities must maintain compliance with Argentina's corporate governance requirements. This includes proper maintenance of corporate record books and accounting documentation, with specific variations based on entity type and provincial location.
The decentralized nature of Argentina's registry system necessitates compliance at both federal and provincial levels, with procedures potentially differing across jurisdictions. This multi-layered approach requires coordinated compliance strategies to ensure ongoing regulatory adherence.
Argentina's business establishment environment continues to evolve, with recent reforms generally trending toward reduced bureaucracy and enhanced transparency. However, the complexity of navigating multiple regulatory layers underscores the value of experienced local counsel to ensure both compliance and strategic alignment with business objectives.
