Colombia's taxation system operates across national and regional levels, creating a structured yet complex environment for businesses and individuals. The division of fiscal authority between national and local governments establishes clear parameters for tax compliance while requiring comprehensive understanding of multiple regulatory frameworks. This overview examines the fundamental aspects of Colombia's tax regime to assist international investors in developing effective tax strategies.
Foundational Principles of Colombian Taxation
The Colombian tax system mandates meticulous accounting practices as the cornerstone of tax compliance. Taxpayers must maintain comprehensive records that accurately reflect assets, liabilities, equity, income, costs, and expenses in accordance with nationally recognized accounting standards. The accrual basis of accounting forms the foundation for tax reporting, requiring recognition of economic events regardless of cash movement timing.
【Lawshi Professional Insight】
The functional currency requirement for tax purposes creates important considerations for international businesses. While the Colombian peso serves as the primary reporting currency, transactions in foreign currencies must be converted using specific methodologies approved by tax authorities. Companies should implement systematic approaches to currency conversion to ensure consistency across financial and tax reporting.
Tax residency rules establish broad taxation parameters for domestic companies and individuals. Entities incorporated in Colombia, those maintaining their principal place of business within the country, or organizations with effective management located in Colombian territory all qualify as domestic taxpayers subject to worldwide income taxation. This comprehensive approach to residency necessitates careful planning for multinational enterprises with Colombian operations.
Core Components of Colombia's Tax System
Income and Capital Gains Taxation
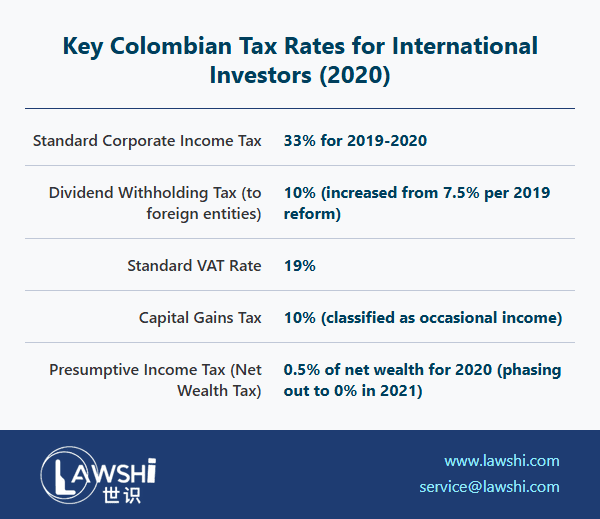
The Colombian income tax framework distinguishes between ordinary business profits and occasional gains, applying different rates to each category. The standard corporate income tax rate has undergone recent adjustments, while occasional gains—defined as profits from non-ordinary activities—face preferential treatment. Special regimes for free trade zone participants offer reduced rates to encourage specific types of investment and economic development.
Value Added Tax Structure
Colombia's VAT system encompasses a broad range of transactions, including sales of movable and immovable goods, specific intellectual property rights transfers, and services rendered within or to Colombian territory. The multi-tiered rate structure categorizes goods and services according to social and economic priorities, with exemptions and reduced rates applying to essential items.
【Lawshi Practical Tip】
VAT compliance requires careful attention to the specific categorization of goods and services, as misclassification can lead to significant liabilities. We recommend maintaining detailed documentation supporting VAT treatment decisions, particularly for transactions involving multiple tax rates or exemptions. Regular reviews of product and service classifications help ensure ongoing compliance as business activities evolve.
Consumption Tax Applications
The national consumption tax applies selectively to specific goods and services deemed non-essential or subject to special regulatory treatment. The tiered rate structure reflects policy priorities across different consumption categories, with higher rates typically applied to luxury items and certain services. Businesses operating in affected sectors must implement precise tracking mechanisms to properly assess and collect these obligations.
Municipal Taxation Requirements
The Industry and Commerce Tax represents a significant local-level obligation for businesses operating across multiple Colombian jurisdictions. Each municipality establishes its own rates within statutory parameters, creating a patchwork of local tax obligations that requires careful coordination. Companies with operations in multiple locations must develop systems to track and comply with these varying local requirements.
Dividend Distribution Framework
Colombia's dividend taxation system has evolved significantly in recent years, creating a layered approach to profit distributions. The current framework distinguishes between dividends paid to domestic and foreign recipients, with varying treatment based on the underlying taxation of distributed earnings. Understanding the timing and characterization of profit distributions is essential for optimizing overall tax outcomes.
【Lawshi Exclusive Service】
Our firm provides comprehensive tax planning services that address both national and municipal tax obligations. We assist clients in structuring operations to optimize tax outcomes across multiple jurisdictions, implementing compliance systems for VAT and consumption taxes, and developing strategies for efficient profit repatriation that consider Colombia's evolving dividend taxation rules.
Strategic Tax Planning Considerations
Colombia's tax environment requires integrated planning that addresses both national and local obligations. The coexistence of multiple tax types—including income, VAT, consumption, and municipal taxes—creates interconnected compliance requirements that benefit from coordinated management. Businesses should develop comprehensive tax control frameworks that address all relevant obligations while maintaining flexibility to adapt to regulatory changes.
The timing of tax obligations varies across different tax types, with income tax calculated annually while other taxes require more frequent reporting and payment. This varied compliance calendar necessitates robust internal processes to ensure all obligations are met within prescribed deadlines. Implementing systematic approaches to tax accounting and compliance helps prevent penalties and interest charges resulting from inadvertent non-compliance.
Emerging Trends and Compliance Priorities
Colombia continues to modernize its tax administration through digital reporting requirements and enhanced verification processes. Businesses should anticipate increasing automation of tax compliance procedures and implement systems capable of meeting evolving electronic reporting standards. Proactive engagement with tax authorities through ruling requests and advance pricing agreements can provide valuable certainty for complex transactions.
The dynamic nature of Colombia's tax system underscores the importance of ongoing monitoring and adaptation. Regular review of tax positions in light of evolving jurisprudence and administrative guidance helps maintain both compliance and optimization. With proper planning and expert guidance, international investors can effectively navigate Colombia's tax landscape while supporting their strategic business objectives.
